Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Analysis to Identify Bone Marrow Dose Constraint Cut-Offs for Predicting Hematological Toxicities in High-Risk Endometrial Cancer
Abstract
Introduction: The new standard of adjuvant treatment (chemotherapy and whole pelvis radiotherapy) in patients with high risk endometrial cancer (EC) was associated to more hematological toxicity.We aimed to identify the predictive bone marrow (BM) dose constraints values for hematological toxicities (HT)≥ 2.
Methodology: Patients with high risk EC treated with adjuvant chemotherapy and VMAT chemoradiation were analysed. Pelvic bones (PB) were delineated from the inferior border of the ischial tuberosities up to 25 mm superior to the PTV. We used the following consensuel bone marrow (BM) doses constraints for plan acceptance : V10 Gy ≤ 90 %, V20 Gy ≤ 75 % and V40 Gy ≤ 37 % . HT were assessed according to the consensus Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 5.0.
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was applied to evaluate the significance of V10 Gy, V20Gy, V30Gy, and V40 Gy on grade 2 or more HT . We displayed the precision, the sensitivity and the specificity. We also visualised the roc curve, and measured the optimal cut-off value and the air under the curve (AUC) then we used a logistic regression model for the z-test in combined detection comparison (P < 0.05 was considered as statistically significant).
Results: Fifty patients were included. Hematological toxicity occurred in 40 patients. Anemia, lymphopenia, neutropenia and thrombocytopenia grades> 2 were observed in 14, 32,17 and 13 patients, respectively. Selected cut-off values for V20Gy (≥ 78,7%, p = 0.057), V30Gy ((≥36,16%, p = 0.011) and V40Gy((≥ 22,78%, p=0.009) appear to have good discriminating power to predict lymphopenia grade ≥ 2 (Table 1).
BM dose constraint values predicting Anemia grade ≥ 2 were V20Gy ((≥ 83,1%, p = 0.019),
V30Gy ((≥ 40,6%, p = 0.03) and V40Gy((≥ 31,27%, p=0.002) (Table 1).
Cut-off values for V30Gy ((≥ 44.4%, p = 0.036), and V40Gy ((≥ 34,64%, p = 0.025)
demonstrate strong discriminatory power in predicting grade 22 neutropenia (Table 1).
Only the cut-off value for V40Gy (≥20.35%, p = 0.03) demonstrates strong discriminative ability in predicting grade ≥2 thrombocytopenia (Table 1).
Conclusion: Adjuvant CT in high-risk EC patients is associated with increased HT of grade ≥ 2. We suggest that the current V40Gy threshold of <35% should be lowered to 20-25%. Additionally, we suggest a new V30Gy constraint, recommending that it be kept below 40-45%.
| Anemia Grade≥ 2 | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mov10gy | 83.684 | 0.696 | 0.444 | 0.857 | 0.437 | 0.012 | ||||||||
| mov20gy | 83.1 | 0.596 | 0.444 | 0.857 | 0.54 | 0.019 | ||||||||
| mov30gy | 40.62 | 0.609 | 0.667 | 0.771 | 0.571 | 0.03 | ||||||||
| mov40gy | 31.27 | 0.652 | 0.444 | 0.786 | 0.63 | 0.002 | ||||||||
| Lymphopenia Grade≥2 | ||||||||||||||
| mov10gy | 87.68 | 0.568 | 0.667 | 0.5 | 0.701 | 0.132 | ||||||||
| mov20gy | 78.7 | 0.667 | 0.571 | 0.778 | 0.646 | 0.057 | ||||||||
| mov30gy | 36.166 | 0.59 | 0.81 | 0.633 | 0.705 | 0.011 | ||||||||
| mov40gy | 22.784 | 0.718 | 0.667 | 0.778 | 0.743 | 0.009 | ||||||||
| Neutropenia Grade≥ 2 | ||||||||||||||
| mov10gy | 82.558 | 0.547 | 0.4 | 1 | 0.557 | 0.062 | ||||||||
| mov20gy | 70.321 | 0.588 | 0.7 | 0.714 | 0.6 | 0.047 | ||||||||
| mov30gy | 44.4 | 0.647 | 0.5 | 0.857 | 0.571 | 0.036 | ||||||||
| mov40gy | 34.64 | 0.706 | 0.3 | 1 | 0.617 | 0.025 | ||||||||
| Thrombocytopenia Grade≥2 | ||||||||||||||
| mov10gy | 83.684 | 0.442 | 1 | 0.667 | 0.581 | 0.289 | ||||||||
| mov20gy | 88.66 | 0.492 | 0.429 | 1 | 0.438 | 0.114 | ||||||||
| mov30gy | 40.912 | 0.669 | 0.857 | 0.667 | 0.514 | 0.088 | ||||||||
| mov40gy | 20.35 | 0.846 | 0.857 | 0.822 | 0.701 | 0.03 | ||||||||
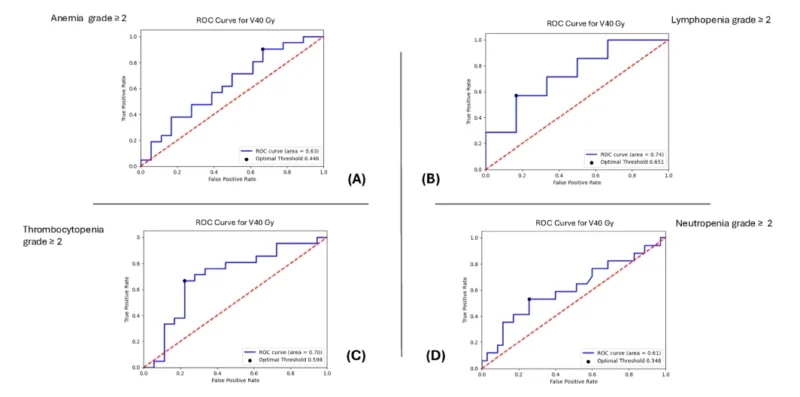
Figure 1: Roc curve of sensitivity versus specificity of V 40 Gy in (A) Anemia grade > 2 toxicity, (B) lymphopenia grade > 2 toxicity, (C) thrombocytopenia grade > 2 and (D) Neutropenia grade > 2 toxicities
Conflict of interests: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Funding: This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
License: ©️ Author(s) 2026. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, and unrestricted adaptation and reuse, including for commercial purposes, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
To view a copy of this license, visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.





